Dengue fever
O'nyong-nyong fever; Dengue-like disease; Breakbone fever
Dengue fever is a virus-caused disease that is spread by mosquitoes.
Causes
Dengue fever is caused by 1 of 4 different but related viruses. It is spread by the bite of mosquitoes, most commonly the mosquito Aedes aegypti , which is found in tropic and subtropic regions. This area includes parts of:
- Indonesian archipelago into northeastern Australia
- South and Central America
- Southeast Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Some parts of the Caribbean
Dengue fever is very rare in the United States. Dengue fever should not be confused with dengue hemorrhagic fever , which is a separate disease caused by the same type of virus, but has much more severe symptoms.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a severe, potentially deadly infection spread by some mosquitos.

Symptoms
Dengue fever begins with a sudden high fever, often as high as 105°F (40.5°C), 4 to 7 days after the infection.
A flat, red rash may appear over most of the body 2 to 5 days after the fever starts. A second rash, which looks like the measles , appears later in the disease. Infected people may have increased skin sensitivity and are very uncomfortable.
Measles
Measles is a very contagious (easily spread) illness caused by a virus.
Other symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Headache (especially behind the eyes)
- Joint aches (often severe)
-
Muscle aches
(often severe)
Muscle aches
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than 1 muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascia are the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea and vomiting
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Nasal stuffiness
Exams and Tests
Tests that may be done to diagnose this condition include:
-
Antibody titer
for dengue virus types
Antibody titer
Antibody titer is a laboratory test that measures the level of antibodies in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count (
CBC
)
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for dengue virus types
-
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsin Alkaline phosph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for dengue fever. Fluids are given if there are signs of dehydration . Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is used to treat a high fever.
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it should. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how muc...

Avoid taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), and naproxen (Aleve). They may increase bleeding problems.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The condition generally lasts a week or more. Although uncomfortable, dengue fever is not deadly. People with the condition should fully recover.
Possible Complications
Untreated, dengue fever may cause the following health problems:
-
Febrile
convulsions
Convulsions
A seizure is the physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term "seizure...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe dehydration
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have traveled in an area where dengue fever is known to occur and you have symptoms of the disease.
Prevention
Clothing, mosquito repellent, and netting can help reduce the risk of mosquito bites that can spread dengue fever and other infections. Limit outdoor activity during mosquito season, especially when they are most active, at dawn and dusk.
References
Thomas SJ, Endy TP, Rothman AL, Barrett AD. Flaviviruses (dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, West Nile encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis, Kyasanur forest disease, Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever, Zika). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 155.
Yacoub S, Garrar J. Dengue. In: Farrar J, Hotez PJ, Junghanss T, Kang G, Lalloo D, White NJ, eds. Manson's Tropical Diseases . 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 15.
-
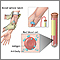
Mosquito, adult feeding on the skin - illustration
There are many different species of mosquito, which can carry some of the world's most common and significant infectious diseases, including West Nile, Malaria, yellow fever, viral encephalitis, and dengue fever. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Mosquito, adult feeding on the skin
illustration
-
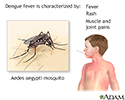
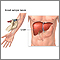
Dengue fever - illustration
Dengue fever, or West Nile fever, is a mild viral illness transmitted by mosquitoes which causes fever, rashes and muscle and joint aches. Treatment includes rehydration and recovery is expected. A second exposure to the virus can result in Dengue hemorrhagic fever, a life-threatening illness.
Dengue fever
illustration
-
Mosquito, adult feeding on the skin - illustration
There are many different species of mosquito, which can carry some of the world's most common and significant infectious diseases, including West Nile, Malaria, yellow fever, viral encephalitis, and dengue fever. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Mosquito, adult feeding on the skin
illustration
-
Dengue fever - illustration
Dengue fever, or West Nile fever, is a mild viral illness transmitted by mosquitoes which causes fever, rashes and muscle and joint aches. Treatment includes rehydration and recovery is expected. A second exposure to the virus can result in Dengue hemorrhagic fever, a life-threatening illness.
Dengue fever
illustration
-
Travel to developing countries
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 9/10/2015
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.