Tracheal rupture
Torn tracheal mucosa; Bronchial rupture
A tracheal or bronchial rupture is a tear or break in the windpipe (trachea) or bronchial tubes, the major airways leading to the lungs. A tear can also occur in the tissue lining the windpipe.
Causes
The injury may be caused by:
- Infections
- Sores (ulcerations) due to foreign objects
- Trauma, such as a gunshot wound or automobile accident
Injuries to the trachea or bronchi also may occur during medical procedures (for example, bronchoscopy and placement of a breathing tube). However, this is very uncommon.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
Symptoms
People with trauma who develop a tracheal or bronchial rupture often have other injuries.
Symptoms may include:
-
Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood is the spitting up of blood or bloody mucus from the lungs and throat (respiratory tract). Hemoptysis is the medical term for cough...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bubbles of air that can be felt underneath the skin of the chest, neck, arms, and trunk (
subcutaneous emphysema
)
Subcutaneous emphysema
Subcutaneous emphysema occurs when air gets into tissues under the skin. This most often occurs in the skin covering the chest wall or neck, but can...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty breathing
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. Close attention will be paid to the symptoms of the rupture.
Tests that may be done include:
- Neck CT scan
-
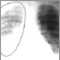
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
People who have had a trauma will need to have their injuries treated. Injuries to the trachea often need to be repaired during surgery. Injuries to the smaller bronchi can sometimes be treated without surgery. A collapsed lung is treated with a chest tube connected to suction, which re-expands the lung.
Collapsed lung
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung, between the lung and chest wall. This bui...
For people who have breathed a foreign body into the airways, bronchoscopy may be used to take out the object.
Antibiotics are used in people with an infection in the part of the lung around the injury.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outlook of injury due to trauma depends on the severity of other injuries. Operations to repair these injuries often have good results. Outlook is good for people whose tracheal or bronchial disruption is due to causes such as a foreign object, which tend to have a good outcome.
In the months or years after the injury, scarring at the injury site may cause problems, such as narrowing, which require other tests or procedures.
Possible Complications
Major complications after surgery for this condition include:
- Infection
- Long-term need of a ventilator
- Narrowing of the airways
- Scarring
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Had a major injury to the chest
- Inhaled a foreign body
- Symptoms of a chest infection
- The feeling of air bubbles underneath your skin and trouble breathing
References
Asensio JA, Trunkey DD. Neck injuries. In: Asensio JA, Trunkey DD, eds. Current Therapy of Trauma and Surgical Critical Care . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:179-185.
Martin RS, Meredith JW. Management of acute trauma. In: Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 16.
-
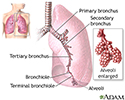
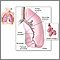
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
Review Date: 8/21/2016
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.