Agoraphobia
Anxiety disorder - agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is an intense fear and anxiety of being in places where it is hard to escape, or where help might not be available. Agoraphobia usually involves fear of crowds, bridges, or of being outside alone.
Causes
The exact cause of agoraphobia is unknown. Agoraphobia sometimes occurs when a person has had a panic attack and begins to fear situations that might lead to another panic attack.
Panic attack
Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder in which you have repeated attacks of intense fear that something bad will happen.
Symptoms
With agoraphobia, you avoid places or situations because you do not feel safe in public places. The fear is worse when the place is crowded.
Symptoms of agoraphobia include:
- Being afraid of spending time alone
- Being afraid of places where escape might be hard
- Being afraid of losing control in a public place
- Depending on others
- Feeling detached or separated from others
- Feeling helpless
- Feeling that the body is not real
- Feeling that the environment is not real
-
Having an unusual temper or
agitation
Agitation
Agitation is an unpleasant state of extreme arousal. An agitated person may feel stirred up, excited, tense, confused, or irritable.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Staying in the house for long periods
Physical symptoms can include:
-
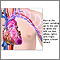
Chest pain
or discomfort
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Choking
-
Dizziness
or
fainting
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea or other stomach distress
- Racing heart
-
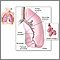
Short of breath
Short of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sweating
Sweating
Sweating is the release of liquid from the body's sweat glands. This liquid contains salt. This process is also called perspiration. Sweating helps...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Trembling
Trembling
A tremor is a type of shaking movement. A tremor is most often noticed in the hands and arms. It may affect any body part, including the head or vo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will look at your history of agoraphobia, and will get a description of the behavior from you, your family, or friends.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to help you feel and function better. The success of treatment usually depends in part on how severe the agoraphobia is. Treatment most often combines talk therapy with a medicine. Certain medicines usually used to treat depression may be helpful for this disorder. They work by preventing your symptoms or making them less severe. You must take these medicines every day. DO NOT stop taking them or change the dosage without talking with your provider.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are most often the first choice of antidepressant.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are another choice.
Other medicines used to treat depression or medicines used to treat seizures may also be tried.
Medicines called sedatives or hypnotics may also be prescribed.
- These medicines should only be taken under a doctor's direction.
- Your doctor will prescribe a limited amount of these drugs. They should not to be used everyday.
- They may be used when symptoms become very severe or when you are about to be exposed to something that always brings on your symptoms.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy. It involves 10 to 20 visits with a mental health professional over several weeks. CBT helps you change the thoughts that cause your condition. It may involve:
- Understanding and controlling distorted feelings or views of stressful events or situations
- Learning stress management and relaxation techniques
- Relaxing, then imagining the things that cause the anxiety, working from the least fearful to the most fearful (called systematic desensitization and exposure therapy)
You may also be slowly exposed to the real-life situation that causes the fear to help you overcome it.
A healthy lifestyle that includes exercise, enough rest, and good nutrition can also be helpful.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of having agoraphobia by joining a support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Support groups are usually not a good substitute for talk therapy or taking medicine, but can be a helpful addition.
Resources for more information include:
Anxiety and Depression Association of America: www.adaa.org
Freedom from Fear: www.freedomfromfear.org
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people can get better with medicines and CBT. Without early and effective help, the disorder may become harder to treat.
Possible Complications
Some people with agoraphobia may:
- Use alcohol or other drugs while trying to self-medicate.
- Be unable to function at work or in social situations.
- Feel isolated, lonely, depressed, or suicidal.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call for an appointment with your provider if you have symptoms of agoraphobia.
Prevention
Early treatment of panic disorder can often prevent agoraphobia.
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders . 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing. 2013.
Calkins AW, Bui E, Taylor CT, Pollack MH, LeBeau RT, Simon NM. Anxiety disorders. In: Stern TA, Fava M, Wilens TE, Rosenbaum JF, eds. Massachusetts General Hospital Comprehensive Clinical Psychiatry . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 32.
Gabbard GO. Generalized anxiety disorder. In: Gabbard GO. Gabbard's Treatments of Psychiatric Disorders . 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2014:chap 19.
-
Panic disorder with agoraphobia - illustration
Panic disorder is characterized by repeated and unpredictable attacks of intense fear and anxiety. Agoraphobia, literally "fear of the marketplace", develops from a panic disorder in more than one-third of cases.
Panic disorder with agoraphobia
illustration
-
Panic disorder with agoraphobia - illustration
Panic disorder is characterized by repeated and unpredictable attacks of intense fear and anxiety. Agoraphobia, literally "fear of the marketplace", develops from a panic disorder in more than one-third of cases.
Panic disorder with agoraphobia
illustration
Review Date: 2/2/2016
Reviewed By: Fred K. Berger, MD, addiction and forensic psychiatrist, Scripps Memorial Hospital, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

