Balanitis
Balanoposthitis
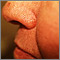
Balanitis is swelling of the foreskin and head of the penis.
Causes
Balanitis is most often caused by poor hygiene in uncircumcised men. Other possible causes include:
-
Diseases such as
reactive arthritis
and lichen sclerosis atrophicus
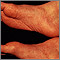
Reactive arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a group of conditions that may involve the joints, eyes, and urinary and genital systems. These areas become swollen and infla...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection
- Harsh soaps
- Not rinsing soap off properly while bathing
- Uncontrolled diabetes
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
-
Redness of foreskin or
penis
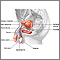
Penis
The penis is the male organ used for urination and sexual intercourse. The penis is located above the scrotum. It is made of spongy tissue and bloo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other rashes on the head of the penis
- Foul-smelling discharge
- Painful penis and foreskin
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider may diagnose the problem with only an exam. However, you may need skin tests for viruses, fungi, or bacteria. A skin biopsy may also be needed.
Skin biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A...
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the balanitis.
- Antibiotic pills or creams are used to treat balanitis that is caused by bacteria.
- Steroid creams may help balanitis that occurs with skin diseases.
- Anti-fungal cream will be prescribed if it is due to a fungus.
In severe cases, circumcision may be the best option. If you cannot pull back (retract) the foreskin to clean it, you may need to be circumcised.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most cases of balanitis can be controlled with medicated creams and good hygiene. Surgery is not needed most of the time.
Possible Complications
Long-term inflammation or infection can:
- Scar and narrow the opening of the penis (meatal stricture)
- Make it difficult and painful to retract the foreskin to expose the tip of the penis (a condition called phimosis)
- Make it difficult to move the foreskin over the head of the penis (a condition called paraphimosis)
- Affect the blood supply to the tip of the penis
- Increase the risk of penile cancer
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Tell your provider if you have any signs of balanitis, including swelling of the foreskin or pain.
Prevention
Good hygiene can prevent most cases of balanitis. When you bathe, pull back the foreskin to clean and dry the area under it.
References
Elder JS. Anomalies of the penis and urethra. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW III, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 544.
Jordan GH, McCammon KA. Surgery of the penis and urethra. In: Wein AJ, ed. Campbell-Walsh Urology . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 36.
Link RE. Cutaneous diseases of the external genitalia. In: Wein AJ, ed. Campbell-Walsh Urology . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 15.
-
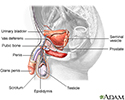
Male reproductive anatomy - illustration
The male reproductive structures include the penis, the scrotum, the seminal vesicles and the prostate.
Male reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
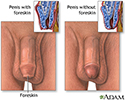
Circumcised vs. uncircumcised - illustration
The penis is covered by a retractable hood of skin called the foreskin, or prepuce. It is the structure which is removed in the procedure known as circumcision.
Circumcised vs. uncircumcised
illustration
-
Male reproductive anatomy - illustration
The male reproductive structures include the penis, the scrotum, the seminal vesicles and the prostate.
Male reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Circumcised vs. uncircumcised - illustration
The penis is covered by a retractable hood of skin called the foreskin, or prepuce. It is the structure which is removed in the procedure known as circumcision.
Circumcised vs. uncircumcised
illustration
Review Date: 8/31/2015
Reviewed By: Jennifer Sobol, DO, urologist at the Michigan Institute of Urology, West Bloomfield, MI. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.