Tabes dorsalis
Locomotor ataxia; Syphilitic myelopathy; Syphilitic myeloneuropathy; Myelopathy - syphilitic; Tabetic neurosyphilis
Tabes dorsalis is a complication of untreated syphilis that involves muscle weakness and abnormal sensations .
Muscle weakness
Weakness is reduced strength in one or more muscles.
Abnormal sensations
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...

Causes
Tabes dorsalis is a form of neurosyphilis , which is a complication of late stage syphilis infection. Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is spread sexually.
Neurosyphilis
Neurosyphilis is a bacterial infection of the brain or spinal cord. It usually occurs in people who have had untreated syphilis for many years....

When syphilis is untreated, the bacteria damages the spinal cord and peripheral nervous tissue. This leads to the symptoms of tabes dorsalis.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is most often spread through sexual contact.

Peripheral
Peripheral means "away from the center. " It refers to areas away from the center of the body or a body part. For example, the hands are peripheral ...
Tabes dorsalis is now very rare because syphilis is usually treated early in the disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms of tabes dorsalis are caused by damage to the nervous system. Symptoms include any of the following:
-
Abnormal sensations (
paresthesia
), often called "lightning pains"
Paresthesia
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Problems walking such as with the legs far apart
- Loss of coordination and reflexes
- Joint damage, especially of the knees
- Muscle weakness
- Vision changes
- Bladder control problems
- Sexual function problems
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam , focusing on the nervous system.
Physical exam
During a physical examination, a health care provider studies your body to determine if you do or do not have a physical problem. A physical examinat...
If syphilis infection is suspected, tests may include the following:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination
A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that in th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Head CT
,
spine CT
, or
MRI
scans of the brain and spinal cord to rule out other diseases
Head CT
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSpine CT
A lumbosacral spine CT is a computed tomography scan of the lower spine and surrounding tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
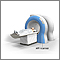
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum VDRL
or serum
RPR
(used as a screening test for syphilis infection)
Serum VDRL
The VDRL test is a screening test for syphilis. It measures substances (proteins), called antibodies, that your body may produce if you have come in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRPR
RPR (rapid plasma reagin) is a screening test for syphilis. It looks for antibodies that are present in the blood of people who may have the disease...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If the serum VDRL or serum RPR test is positive, one of the following tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis:
- FTA-ABS
- MHA-TP
- TP-EIA
- TP-PA
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to cure the infection and slow the disease. Treating the infection helps prevent new nerve damage and may reduce symptoms. Treatment does not reverse existing nerve damage.
Medicines likely to be given include:
- Penicillin or other antibiotics for a long time to make sure the infection goes away
- Painkillers to control pain
Symptoms of existing nervous system damage need to be treated. People who are unable to eat, dress themselves, or take care of themselves may need help. Rehabilitation, physical therapy, and occupational therapy may help with muscle weakness.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Left untreated, tabes dorsalis may lead to disability.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Blindness
- Paralysis
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have:
-
Loss of coordination
Loss of coordination
Uncoordinated movement is due to a muscle control problem that causes an inability to coordinate movements. It leads to a jerky, unsteady, to-and-fr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of muscle strength
-
Loss of sensation
Loss of sensation
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Prevention
Proper treatment and follow-up of syphilis infections reduces the risk of developing tabes dorsalis.
If you are sexually active, practice safer sex and always use a condom.
All pregnant women should be screened for syphilis.
References
Hook EW. Syphilis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 319.
Radolf JD,Tramont EC, Salazar JC. Syphilis ( Treponema pallidum ). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Updated Edition . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 239.
-
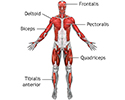
Superficial anterior muscles - illustration
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.
Superficial anterior muscles
illustration
Review Date: 7/31/2016
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.