Neurosarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis - nervous system
Neurosarcoidosis is a complication of sarcoidosis , in which inflammation occurs in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas of the nervous system.
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, or other tissues.
Causes
Sarcoidosis is a long-term disorder that affects many parts of the body, mostly the lungs. In a small number of patients, the disease involves some part of the nervous system. This is called neurosarcoidosis.
Neurosarcoidosis may affect any part of the nervous system. Sudden, facial weakness ( facial palsy ) is a common neurological symptom that involves the nerves to the muscles of the face. Any other nerve in the skull can be affected, including those in the eye and those that control taste, smell, or hearing.
Facial palsy
Bell palsy is a disorder of the nerve that controls movement of the muscles in the face. This nerve is called the facial or seventh cranial nerve. D...

The spinal cord is another part of the nervous system that sarcoid can affect. People may have weakness in their arms and legs, and difficulty walking or controlling their urine.
The condition can also affect the parts of the brain involved in regulating many body functions, such as temperature, sleep, and stress responses.
Muscle weakness or sensory losses can occur with peripheral nerve involvement. Other areas of the brain, including the pituitary gland at the base of the brain, or the spinal cord may also be involved.
Muscle weakness
Weakness is reduced strength in one or more muscles.
Peripheral
Peripheral means "away from the center. " It refers to areas away from the center of the body or a body part. For example, the hands are peripheral ...
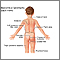
Symptoms
Involvement of the pituitary gland can cause:
- Changes in menstrual periods
-
Excessive tiredness
or fatigue
Excessive tiredness
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Excessive thirst
Excessive thirst
Excessive thirst is an abnormal feeling of always needing to drink fluids.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
High urine output
High urine output
Excessive amount of urination means that your body makes larger than normal amounts of urine each day.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The symptoms vary. Any part of the nervous system can be affected. Involvement of the brain or cranial nerves can cause:
-
Confusion
, disorientation
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
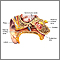
Decreased hearing
Decreased hearing
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, language, judgment, and behavior.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Delirium
Delirium
Delirium is sudden severe confusion due to rapid changes in brain function that occur with physical or mental illness.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dizziness
,
vertigo
, or abnormal sensations of movement
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleVertigo
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Double vision or other vision problems
- Facial palsy (weakness, drooping)
- Headache
-
Loss of sense of smell
Loss of sense of smell
Impaired smell is the partial or total loss or abnormal perception of the sense of smell.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Loss of sense of taste
,
abnormal tastes
Loss of sense of taste
Taste impairment means there is a problem with your sense of taste. Problems range from distorted taste to a complete loss of the sense of taste. A...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbnormal tastes
Taste impairment means there is a problem with your sense of taste. Problems range from distorted taste to a complete loss of the sense of taste. A...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Psychiatric disturbances
-
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term "seizure...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Speech impairment
Involvement of one or more peripheral nerves can lead to:
Peripheral
Peripheral means "away from the center. " It refers to areas away from the center of the body or a body part. For example, the hands are peripheral ...

-
Abnormal sensations
in any body part
Abnormal sensations
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Loss of movement
of any body part
Loss of movement
Muscle function loss is when a muscle does not work or move normally. The medical term for complete loss of muscle function is paralysis.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Loss of sensation
in any body part
Loss of sensation
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness of any body part
Exams and Tests
An exam may show problems with one or more nerves.
A history of sarcoidosis followed by nerve-related symptoms highly suggests neurosarcoidosis. However, symptoms of the condition can mimic other medical disorders, including diabetes insipidus , hypopituitarism , optic neuritis , meningitis , and certain tumors. Sometimes, the nervous system can be affected before a person is known to have sarcoid, or without affecting the lungs or other organs at all.
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus is an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water.

Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a condition in which the pituitary gland does not produce normal amounts of some or all of its hormones.

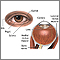
Optic neuritis
The optic nerve carries images of what the eye sees to the brain. When this nerve become swollen or inflamed, it is called optic neuritis. It may c...
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.

Blood tests are not very helpful in diagnosing the condition. A lumbar puncture may show signs of inflammation. Increased levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme may be found in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). However, this is not a reliable diagnostic test.
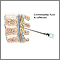
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
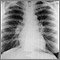
MRI of the brain may be helpful. A chest x-ray often reveals signs of sarcoidosis of the lungs. Nerve biopsy of affected nerve tissue confirms the disorder.
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
Nerve biopsy
A nerve biopsy is the removal of a small piece of a nerve for examination.
Treatment
There is no known cure for sarcoidosis. Treatment is given if symptoms are severe or are getting worse. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms.
Corticosteroids such as prednisone are prescribed to reduce inflammation. They are often prescribed until symptoms get better or go away. You may need to take the medicines for months, or even years.
Other medications may include hormone replacement and medicines that suppress the immune system.
If you have numbness, weakness, vision or hearing problems, or other problems due to damage of the nerves in the head, you may need physical therapy, braces, a cane, or a walker.
Psychiatric disorders or dementia may require medication for depression, safety interventions, and assistance with care.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Some cases go away on their own in 4 - 6 months. Others continue off and on for the rest of the person's life. Neurosarcoidosis can cause permanent disability and, in some cases, death.
Possible Complications
Complications vary depending on which part of the nervous system is involved and how you respond to treatment. Slowly worsening or permanent loss of neurological function is possible. In rare cases, the brainstem may be involved. This is life threatening.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have sarcoidosis and any neurological symptoms occur.
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if you have a sudden loss of sensation, movement, or body function.
Prevention
Aggressive treatment of sarcoidosis turns off the body's faulty immune response before your nerves become damaged. This may reduce the chance that neurological symptoms will occur.
References
Aminoff MJ, Josephson SA. Neurological complications of systemic disease: adults. In: Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, eds. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 49A.
Iannuzzi M. Sarcoidosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 95.
-
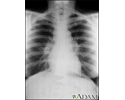
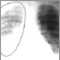
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid is primarily a lung (pulmonary) disease. In the early stages, a chest film may show enlargement of lymph nodes in the center of the chest near the heart (mediastinum).
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray
illustration
-
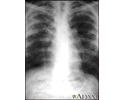
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid causes damage to the lung tissue that heals by scarring. The film shows a diffuse milky and granular appearance in the normally dark lung areas. This individual has marked decrease in lung function.
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray
illustration
-
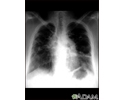
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest X-ray - illustration
This film shows advanced sarcoid, scarring of the lungs (the light streaking), and cavity formation (the dark areas in the upper right side of the picture).
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest X-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid is primarily a lung (pulmonary) disease. In the early stages, a chest film may show enlargement of lymph nodes in the center of the chest near the heart (mediastinum).
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid causes damage to the lung tissue that heals by scarring. The film shows a diffuse milky and granular appearance in the normally dark lung areas. This individual has marked decrease in lung function.
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest X-ray - illustration
This film shows advanced sarcoid, scarring of the lungs (the light streaking), and cavity formation (the dark areas in the upper right side of the picture).
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest X-ray
illustration
Review Date: 2/19/2015
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.