Neuropathy secondary to drugs
Neuropathy secondary to drugs is a loss of sensation or movement in a part of the body due to nerve damage from a certain medicine.
Loss of sensation
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...

Causes
The damage is caused by the toxic effects of certain medicines on the peripheral nerves (nerves that are not in the brain or spinal cord). There may be damage to the axon part of the nerve cell, which interferes with nerve signals.
Peripheral
Peripheral means "away from the center. " It refers to areas away from the center of the body or a body part. For example, the hands are peripheral ...
Most commonly, many nerves are involved (polyneuropathy). This usually causes sensation changes that begin in the outside parts of the body ( distal ) and move toward the center of the body ( proximal ). There may also be changes in movement, such as weakness.
Distal
Distal refers to sites located away from a specific area, usually the center of the body. In medicine, it refers to parts of the body further away f...
Proximal
Proximal means nearer to the center (trunk of the body) or to the point of attachment to the body. If another reference point is given, such as the ...

Many medicines may affect the development of neuropathy, including:
Heart or blood pressure drugs:
- Amiodarone
- Hydralazine
- Perhexiline
Drugs used to fight cancer :
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
- Cisplatin
- Docetaxel
- Paclitaxel
- Suramin
- Vincristine
Drugs used to fight infections:
- Chloroquine
-
Isoniazid (INH), used against
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Metronidazole (Flagyl)
- Nitrofurantoin
-
Thalidomide (used to fight
leprosy
)
Leprosy
Leprosy is an infectious disease that has been known since biblical times. This disease causes skin sores, nerve damage, and muscle weakness that ge...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Drugs used to treat autoimmune disease:
- Etanercept
- Infliximab
- Leflunomide
Drugs used to treat skin conditions (Dapsone)
Anticonvulsants (phenytoin)
Anti-alcohol drugs (disulfiram)
Drugs to fight HIV:
- Didanosine (Videx)
- Stavudine (Zerit)
- Zalcitabine (Hivid)
Arsenic
Colchicine
Gold
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
-
Numbness
,
loss of sensation
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLoss of sensation
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Tingling
,
abnormal sensations
Tingling
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbnormal sensations
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness
Sensation changes usually begin in the feet or hands and move inward.
Exams and Tests
A brain and nervous system examination will be done.
Other tests include:
- Blood tests to check levels of the medicine (even normal blood levels of certain drugs may be toxic in elderly or certain other persons)
-
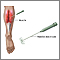
EMG
and
nerve conduction test
of the electrical activity of nerves and muscles
EMG
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleNerve conduction test
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment is based on the symptoms and how severe they are. The drug causing the neuropathy may be stopped, reduced in dose, or changed to another drug. (Never change any drug without first talking to your health care provider).
The following drugs may be used to control pain:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers may be helpful for mild pain (neuralgia).
- Phenytoin, carbamazepine, gabapentin, pregabalin, duloxetine, or tricyclic antidepressants such as nortriptyline may reduce the stabbing pains some people experience.
- Opiate pain relievers, such as morphine or fentanyl, may be needed to control severe pain.
Whenever possible, avoid or reduce use of medicines to lessen the risk of side effects.
There are currently no medicines that can reverse the loss of sensation. If you have lost sensation, you may need to take safety measures to avoid injury.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Many people can partially or fully return to their normal function. The disorder does not usually cause life-threatening complications, but it can be uncomfortable or disabling.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Inability to function at work or home because of permanent loss of sensation
- Pain with tingling in the area of the nerve injury
- Permanent loss of sensation (or rarely, movement) in an area
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have a loss of sensation or movement of any area of the body while taking any medicine.
Prevention
Your provider will closely monitor your treatment with any drug that may cause neuropathy. The goal is to keep the proper blood level of the drug needed to control the disease and its symptoms while preventing the drug from reaching toxic levels.
References
Katirji B, Koontz D. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 76.
Staff NP, Windebank AJ. Peripheral neuropathy due to vitamin deficiency, toxins, and medications. Continuum (Minneap Minn) . 2014;20(5 Peripheral Nervous System Disorders):1293-1306. PMID: 25299283 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25299283 .
Weimer LH, Sachdev N. Update on medication-induced peripheral neuropathy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep . 2009;9:69-75. PMID: 19080756 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19080756 .
-
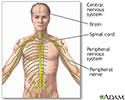
Central nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Central nervous system
illustration
-
Diabetes - type 2
(In-Depth)
-
Lymphoma
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Hodgkin disease
(In-Depth)
-
Restless legs syndrome and related disorders
(In-Depth)
-
Lyme disease and related tick-borne infections
(In-Depth)
-
Hypothyroidism
(In-Depth)
-
Erectile dysfunction
(In-Depth)
-
Gout
(In-Depth)
-
Peripheral artery disease and intermittent claudication
(In-Depth)
-
Colon and rectal cancers
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 2/3/2015
Reviewed By: Amit M. Shelat, DO, FACP, Attending Neurologist and Assistant Professor of Clinical Neurology, SUNY Stony Brook, School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.