Congenital protein C or S deficiency
Protein S deficiency; Protein C deficiency
Congenital protein C or S deficiency is a lack of proteins C or S in the fluid part of the blood. The proteins are natural substances that help prevent blood clots.
Causes
Congenital protein C or S deficiency is an inherited disorder. This means it is passed down through families. Congenital means it is present at birth.
The disorder causes abnormal blood clotting.
One in 300 people has one normal gene and one faulty gene for protein C deficiency.
Protein S deficiency is much less common and occurs in about 1 in 20,000 people.
Symptoms
If you have this condition, you are more likely to develop blood clots. The symptoms are the same as for deep vein thrombosis , and include:
Deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein deep inside a part of the body. It mainly affects the large ...
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
-
Redness or
swelling
in the affected area
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
Laboratory tests will be done to check for proteins C and S.
Treatment
Blood-thinning drugs are used to treat and prevent blood clots.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is usually good with treatment, but symptoms may return, especially if blood-thinning agents are stopped.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
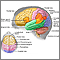
Childhood
stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - More than one pregnancy loss (recurrent miscarriage)
- Recurrent clots in the veins
-
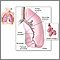
Pulmonary embolism
(blood clot in a lung artery)
Pulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolus is a blockage of an artery in the lungs. The most common cause of the blockage is a blood clot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
In rare cases, using warfarin to thin the blood and prevent clots can cause brief increased clotting and severe skin wounds. People are at risk if they are not treated with the blood-thinning drug heparin before taking warfarin.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have symptoms of clotting in a vein (swelling and redness of the leg).
Prevention
If your provider diagnoses you with this disorder, you should be careful to prevent clots from forming. This can occur when the blood moves slowly in the veins, such as from prolonged bed rest during an illness, surgery, or hospital stay. It may also occur after long airplane or car trips.
References
Anderson JA, Weitz JI. Hypercoagulable states. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Silberstein LE, Heslop HE, Weitz JI, Anastasi J, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:chap 142.
-
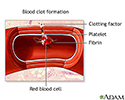
Blood clot formation - illustration
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to adhere to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed, and the external bleeding stops. Next, small molecules, called clotting factors, cause strands of blood-borne materials, called fibrin, to stick together and seal the inside of the wound. Eventually, the cut blood vessel heals and the blood clot dissolves after a few days.
Blood clot formation
illustration
-
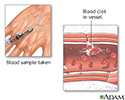
Blood clots - illustration
Blood clots (fibrin clots) are the clumps that result when blood coagulates.
Blood clots
illustration
-
Blood clot formation - illustration
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to adhere to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed, and the external bleeding stops. Next, small molecules, called clotting factors, cause strands of blood-borne materials, called fibrin, to stick together and seal the inside of the wound. Eventually, the cut blood vessel heals and the blood clot dissolves after a few days.
Blood clot formation
illustration
-
Blood clots - illustration
Blood clots (fibrin clots) are the clumps that result when blood coagulates.
Blood clots
illustration
Review Date: 11/10/2016
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.