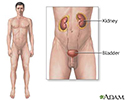
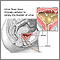
Nephrocalcinosis
Nephrocalcinosis is a disorder in which there is too much calcium deposited in the kidneys. It is common in premature babies.
Causes
Any disorder that leads to high levels of calcium in the blood or urine may lead to nephrocalcinosis. In nephrocalcinosis, calcium deposits form in the kidney tissue itself. Most of the time, both kidneys are affected.
Nephrocalcinosis is related to, but not the same as, kidney stones (nephrolithiasis).
Kidney stones
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
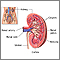
Conditions that can cause nephrocalcinosis include:
-
Alport syndome
Alport syndome
Alport syndrome is an inherited disorder that damages the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys. It also causes hearing loss and eye problems.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bartter syndrome
Bartter syndrome
Bartter syndrome is a group of rare conditions that affect the kidneys.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic
glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease in which the part of your kidneys that helps filter waste and fluids from the blood is damaged....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Familial hypomagnesemia
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Primary hyperoxaluria
- Renal transplant rejection
-
Renal tubular acidosis
Renal tubular acidosis
Proximal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys don't properly remove acids from the blood into the urine. As a result, to...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Renal
cortical
necrosis
Renal
The term "renal" refers to the kidney. For example, renal failure means kidney failure. Related topics:Kidney diseaseKidney disease - dietKidney fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleNecrosis
Necrosis is the death of body tissue. It occurs when too little blood flows to the tissue. This can be from injury, radiation, or chemicals. Necro...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other possible causes of nephrocalcinosis include:
- Ethylene glycol toxicity
-
Hypercalcemia
(excess calcium in the blood) due to
hyperparathyroidism
Hypercalcemia
Ionized calcium is calcium in your blood that is not attached to proteins. It is also called free calcium. All cells need calcium in order to work. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a disorder in which the parathyroid glands in your neck produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of certain medicines, such as acetazolamide, amphotericin B, and triamterene
- Sarcoidosis
-
Tuberculosis
of the kidney and infections related to AIDS
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vitamin D toxicity
Symptoms
Most of the time, there are no early symptoms of nephrocalcinosis beyond those of the condition causing the problem.
People who also have kidney stones may have:
-
Blood in the urine
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe pain in the belly area, sides of the back (flank), groin, or testicles
Later symptoms related to nephrocalcinosis may be associated with chronic kidney failure .
Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...

Exams and Tests
Nephrocalcinosis may be discovered when symptoms of renal insufficiency , kidney failure , obstructive uropathy, or urinary tract stones develop.
Renal insufficiency
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...

Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...

Urinary tract stones
Bladder stones are hard buildups of minerals. These form in the urinary bladder.

Imaging tests can help diagnose this condition. Tests that may be done include:
-
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging method. This test uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomog...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ultrasound
of the kidney
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests that may be done to diagnose and determine the severity of associated disorders include:
- Blood tests to check levels of calcium, phosphate, uric acid, and parathyroid hormone
-
Urinalysis
to see crystals and check for red blood cells
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - 24-hour urine collection to measure acidity and levels of calcium, sodium, uric acid, oxalate, and citrate
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms and prevent more calcium from building up in the kidneys.
Treatment will involve methods to reduce abnormal levels of calcium, phosphate, and oxalate in the blood and urine. Options include making changes in your diet and taking medicines and supplements.
If you take medicine that causes calcium loss, your health care provider will most often tell you to stop taking it. Never stop taking any medicine before talking to your provider.
Other symptoms, including kidney stones, should be treated as is appropriate.
Outlook (Prognosis)
What to expect depends on the complications and cause of the disorder.
Proper treatment may help prevent further deposits in the kidneys. In most cases, there is no way to remove deposits that have already formed. Many deposits of calcium in the kidneys do NOT always mean severe damage to the kidneys.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Acute renal failure
Acute renal failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney stones
Kidney stones
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Obstructive uropathy
(acute or chronic, unilateral or bilateral)
Obstructive uropathy
Obstructive uropathy is a condition in which the flow of urine is blocked. This causes the urine to back up back up and injure one or both kidneys....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you know you have a disorder that causes high levels of calcium in your blood and urine. Also call you if you develop symptoms of nephrocalcinosis.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of disorders that lead to nephrocalcinosis, including renal tubular acidosis , may help prevent it from developing.
Renal tubular acidosis
Proximal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys don't properly remove acids from the blood into the urine. As a result, to...

References
Bushinsky DA. Nephrolithiasis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 126.
Elder JS. Urinary lithiasis. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 547.
Review Date: 8/31/2015
Reviewed By: Jennifer Sobol, DO, urologist at the Michigan Institute of Urology, West Bloomfield, MI. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.