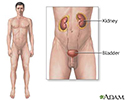
Lupus nephritis
Nephritis - lupus; Lupus glomerular disease
Lupus nephritis is a kidney disorder which is a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus .
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It can af...
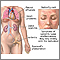
Causes
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus) is an autoimmune disease . This means there is a problem with the body's immune system.
Autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 types of aut...
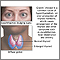
Normally, the immune system helps protect the body from infection or harmful substances. But in people with an autoimmune disease, the immune system cannot tell the difference between harmful substances and healthy ones. As a result, the immune system attacks otherwise healthy cells and tissues.
SLE may damage different parts of the kidney. This can lead lead to disorders such as interstitial nephritis , nephrotic syndrome , and membranous glomerulonephritis . Over time, kidney failure can result.
Interstitial nephritis
Interstitial nephritis is a kidney disorder in which the spaces between the kidney tubules become swollen (inflamed). This can cause problems with t...
Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a group of symptoms that include protein in the urine, low blood protein levels in the blood, high cholesterol levels, high tri...

Membranous glomerulonephritis
Membranous nephropathy is a kidney disorder that leads to changes and inflammation of the structures inside the kidney that help filter wastes and fl...
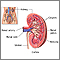
Symptoms
Symptoms of lupus nephritis include:
-
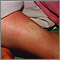
Blood in the urine
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Foamy appearance to urine
- High blood pressure
-
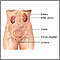
Swelling
of any area of the body
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A physical exam shows signs of decreased kidney functioning with body swelling (edema). Blood pressure may be high. Abnormal sounds may be heard when the doctor listens to your heart and lungs.
Tests that may be done include:
-
ANA
titer
ANA
The antinuclear antibody panel is a blood test that looks at antinuclear antibodies (ANA). ANA are substances produced by the immune system that atta...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
BUN
and
creatinine
BUN
BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen. Urea nitrogen is what forms when protein breaks down. A test can be done to measure the amount of urea nitrogen ...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCreatinine
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine can ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complement
levels
Complement
Complement is a blood test that measures the activity of certain proteins in the liquid portion of your blood. The complement system is a group of pr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine protein
-
Kidney biopsy
, to determine appropriate treatment
Kidney biopsy
A kidney biopsy is the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to improve kidney function and to delay kidney failure.
Medicines may include drugs that suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, or azathioprine.
You may need dialysis to control symptoms of kidney failure, sometimes for only a while. A kidney transplant may be recommended. People with active lupus should not have a transplant because the condition can occur in the transplanted kidney.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do, depends on the specific form of lupus nephritis. You may have flare-ups, and then times when you do not have any symptoms.
Some people with this condition develop chronic kidney failure.
Although lupus nephritis may return in a transplanted kidney, it rarely leads to end-stage kidney disease.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result from lupus nephritis include:
-
Acute renal failure
Acute renal failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have blood in the urine or swelling of your body.
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...

Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...

If you have lupus nephritis, call your provider if you notice decreased urine output .
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 ml of urine in 24 hours (a little over 2 cups)....

Prevention
Treating lupus may help prevent or delay onset of lupus nephritis.
References
Appel GB, Jayne D, Rovin BH. Lupus nephritis. In: Johnson RJ, Feehally J, Floege J, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 26.
Hahn BH, McMahon M, Wilkinson A, et al. American College of Rheumatology Guidelines for Screening, Case Definition, Treatment and Management of Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) . 2012;64(6):797-808. PMC:3437757 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3437757 .
Review Date: 9/22/2015
Reviewed By: Charles Silberberg, DO, private practice specializing in nephrology, affiliated with New York Medical College, Division of Nephrology, Valhalla, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.