Toxic nodular goiter
Toxic multinodular goiter; Plummer disease; Thyrotoxicosis - nodular goiter; Overactive thyroid - toxic nodular goiter; Hyperthyroidism - toxic nodular goiter; Toxic multinodular goiter; MNG
Toxic nodular goiter involves an enlarged thyroid gland. The gland contains areas that have increased in size and formed nodules. One or more of these nodules produce too much thyroid hormone.
Causes
Toxic nodular goiter starts from an existing simple goiter . It occurs most often in older adults. Risk factors include being female and over 55 years old. This disorder is rare in children. Most people who develop it have had a goiter with nodules for many years.
Simple goiter
A simple goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. It is usually not a tumor or cancer.
Sometimes, people with toxic multinodular goiter will develop high thyroid levels for the first time. This mostly occurs after they take in a large amount of iodine through a vein (intravenously) or by mouth. The iodine may be used as contrast for a CT scan or heart catheterization . Taking medicines that contain iodine, such as amiodarone, may also lead to the disorder.
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

Heart catheterization
Cardiac catheterization involves passing a thin flexible tube (catheter) into the right or left side of the heart. The catheter is most often insert...
Symptoms
Symptoms are the same as those of an overactive thyroid gland ( hyperthyroidism ). However, the bulging eyeballs seen in Graves disease do not occur.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.

Graves disease
Graves disease is an autoimmune disorder that leads to an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism). An autoimmune disorder is a condition that occ...

Symptoms may include any of the following:
-
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Frequent bowel movements
-
Heat intolerance
Heat intolerance
Heat intolerance is a feeling of being overheated when the temperature around you rises. It can often cause heavy sweating. Heat intolerance usually...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased appetite
- Increased sweating
- Irregular menstrual period (in women)
-
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nervousness
-
Restlessness
Restlessness
Agitation is an unpleasant state of extreme arousal. An agitated person may feel stirred up, excited, tense, confused, or irritable.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight loss
Exams and Tests
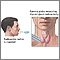
A physical examination will show 1 or many nodules in the thyroid. There may be a rapid heart rate .
Physical examination
During a physical examination, a health care provider studies your body to determine if you do or do not have a physical problem. A physical examinat...
Nodules
Skin nodules are solid or cystic raised bumps in the skin that are wider than 1 centimeter (cm), but less than 2 cm.
Rapid heart rate
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat.

Other tests that may be done include:
-
Serum thyroid hormone levels (
T3
,
T4
)
T3
Triiodothyronine (T3) is a thyroid hormone. It plays an important role in the body's control of metabolism (the many processes the body does to func...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleT4
T4 (thyroxine) is the main hormone produced by the thyroid gland. A laboratory test can be done to measure the amount of free T4 in your blood....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum TSH
(thyroid stimulating hormone)
Serum TSH
A TSH test measures the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland. It tells the thyroid gla...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thyroid uptake and scan
or
radioactive iodine uptake
Thyroid uptake and scan
A thyroid scan uses a radioactive iodine tracer to examine the structure and function of the thyroid gland. This test is often done together with a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRadioactive iodine uptake
Radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) tests thyroid function. It measures how much radioactive iodine is taken up by your thyroid gland in a certain time...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound
A thyroid ultrasound is an imaging method to see the thyroid, a gland in the neck that regulates metabolism.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Beta-blockers (propranolol) can control some of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism until thyroid hormone levels in the body are under control.
Certain drugs can block or change how the thyroid gland uses iodine. These drugs may be used to control the overactive thyroid gland in any of the following cases:
- Before surgery or radioiodine therapy occurs
- As a long term treatment
Radioiodine therapy may be used. Radioactive iodine is given by mouth. It then concentrates in the overactive thyroid tissue and causes damage. Some people, but not all, may need to take thyroid replacement afterwards.
Surgery to remove the thyroid may be done when:
- Very large goiter or a goiter is causing symptoms by blocking the airway
- Thyroid cancer is present
- Rapid treatment is needed
Outlook (Prognosis)
Toxic nodular goiter is mainly a disease of older adults, so other chronic health problems may affect the outcome of this condition. An older adult may be less able to tolerate the effect of the disease on the heart. However, the condition is often treatable with medicines.
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...

Possible Complications
Heart complications:
-
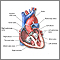
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Irregular heartbeat (
atrial fibrillation
)
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation or flutter is a common type of abnormal heartbeat. The heart rhythm is fast and most often irregular.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rapid heart rate
Other complications:
-
Bone loss leading to
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Thyroid crisis or storm is an acute worsening of hyperthyroidism symptoms. It may occur with infection or stress . Thyroid crisis may cause:
Acute
Acute means sudden or severe. Acute symptoms appear, change, or worsen rapidly. It is the opposite of chronic.

Stress
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...

- Abdominal pain
- Decreased mental alertness
- Fever
People with this condition need to go to the hospital right away.
Complications of having a very large goiter may include difficulty breathing or swallowing. These complications are due to pressure on the airway passage (trachea) or esophagus, which lies behind the thyroid.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have symptoms of this disorder. Follow the provider's instructions for follow-up visits.
Prevention
To prevent toxic nodular goiter, treat hyperthyroidism and simple goiter as your provider suggests.
References
Hegedus L, Paschke R, Krohn K, Bonnema SJ. Multinodular goiter. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, et al, eds. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 90.
Kim M, Ladenson PW. Thyroid. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 226.
Kopp P. Autonomously functioning thyroid nodules and other causes of thyrotoxicosis. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, et al, eds. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 85.
-
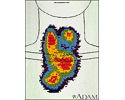
Thyroid enlargement - scintiscan - illustration
This image shows enlargement of the thyroid gland and extension down behind the breastbone (retrosternal space). The image, called a scintiscan, was generated using a radioactive isotope.
Thyroid enlargement - scintiscan
illustration
-
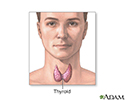
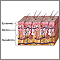
Thyroid gland - illustration
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Thyroid gland
illustration
-
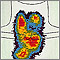
Thyroid enlargement - scintiscan - illustration
This image shows enlargement of the thyroid gland and extension down behind the breastbone (retrosternal space). The image, called a scintiscan, was generated using a radioactive isotope.
Thyroid enlargement - scintiscan
illustration
-
Thyroid gland - illustration
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Thyroid gland
illustration
Review Date: 2/3/2016
Reviewed By: Brent Wisse, MD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology & Nutrition, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.