Choledocholithiasis
Gallstone in the bile duct; Bile duct stone
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of at least one gallstone in the common bile duct. The stone may be made up of bile pigments or calcium and cholesterol salts.
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...

Causes
About 1 in 7 people with gallstones will develop stones in the common bile duct. This is the small tube that carries bile from the gallbladder to the intestine.
Risk factors include a history of gallstones . However, choledocholithiasis can occur in people who have had their gallbladder removed.
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. Gallstones may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.

Symptoms
Often, there are no symptoms unless the stone blocks the common bile duct. Symptoms may include:
- Pain in the right upper or middle upper abdomen for at least 30 minutes. The pain may be constant or cramping. It can feel sharp or dull.
-
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Yellowing of skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Loss of appetite
-
Nausea
and
vomiting
Nausea
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up is forcing the contents of the stomach ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleVomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up is forcing the contents of the stomach ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Clay-colored stools
Exams and Tests
Tests that show the location of stones in the bile duct include the following:
-
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging method. This test uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomog...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
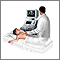
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
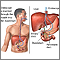
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography
(ERCP)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography
ERCP is short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. It is a procedure that looks at the bile ducts. It is done through an endoscope. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Endoscopic ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
-
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA)
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram...
A percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA) is an x-ray of the bile ducts. These are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladde...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Your health care provider may order the following blood tests:
-
Bilirubin
Bilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count
(CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsin Alkaline phosph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pancreatic
enzymes
Enzymes
Enzymes are complex proteins that cause a specific chemical change in all parts of the body. For example, they can help break down the foods we eat ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve the blockage.
Treatment may involve:
- Surgery to remove the gallbladder and stones
-
ERCP
and a procedure called a sphincterotomy, which makes a surgical cut into the muscle in the common bile duct to allow stones to pass or be removed
ERCP
ERCP is short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. It is a procedure that looks at the bile ducts. It is done through an endoscope. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Outlook (Prognosis)
Blockage and infection caused by stones in the biliary tract can be life-threatening. Most of the time, the outcome is good if the problem is detected and treated early.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Biliary
cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cholangitis
Cholangitis
Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile is a liquid made by ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pancreatitis
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
- You develop abdominal pain, with or without fever, and there is no known cause.
- You develop jaundice.
- You have other symptoms of choledocholithiasis.
References
Fogel EL, Sherman S. Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 155.
Jackson PG, Evans SRT. Biliary system. In: Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 18th ed. St. Louis, MO: WB Saunders; 2012:chap 55.
-
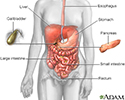
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
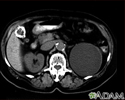
Kidney cyst with gallstones, CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a fist-sized cyst of the left kidney and gallstones (the kidney cyst was found by chance; there were no symptoms).
Kidney cyst with gallstones, CT scan
illustration
-
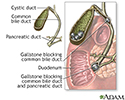
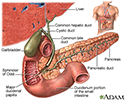
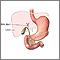
Choledocholithiasis - illustration
About 15% of people with gallstones will develop stones in the common bile duct. The common bile duct is a small tube that carries bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum. Obstruction of the common bile duct may also lead to obstruction of the pancreatic duct because these ducts are usually connected. If the pancreatic duct is also obstructed, pancreatitis will likely develop.
Choledocholithiasis
illustration
-
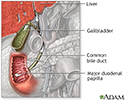
Gallbladder - illustration
The liver produces bile which aids in the digestion of fats. The bile travels through tiny canals which eventually drain through the common bile duct into the small intestine. The gallbladder stores excess bile that is not immediately needed for digestion.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
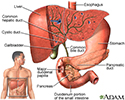
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a muscular sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver that is not immediately needed for digestion. Bile is released from the gallbladder into the small intestine in response to food. The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct at the small intestine adding enzymes to aid in digestion.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Kidney cyst with gallstones, CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a fist-sized cyst of the left kidney and gallstones (the kidney cyst was found by chance; there were no symptoms).
Kidney cyst with gallstones, CT scan
illustration
-
Choledocholithiasis - illustration
About 15% of people with gallstones will develop stones in the common bile duct. The common bile duct is a small tube that carries bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum. Obstruction of the common bile duct may also lead to obstruction of the pancreatic duct because these ducts are usually connected. If the pancreatic duct is also obstructed, pancreatitis will likely develop.
Choledocholithiasis
illustration
-
Gallbladder - illustration
The liver produces bile which aids in the digestion of fats. The bile travels through tiny canals which eventually drain through the common bile duct into the small intestine. The gallbladder stores excess bile that is not immediately needed for digestion.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a muscular sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver that is not immediately needed for digestion. Bile is released from the gallbladder into the small intestine in response to food. The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct at the small intestine adding enzymes to aid in digestion.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
-
Gallstones and gallbladder disease
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 4/20/2015
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist at Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.