Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJS) is a disorder passed down through families (inherited). In this condition, you may have mild jaundice throughout life.
Causes
DJS is a very rare genetic disorder. In order to inherit the condition, a child must get a copy of the defective gene from both parents.
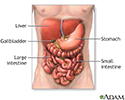
The syndrome interferes with the body's ability to move bilirubin from the liver. When the liver breaks down worn out red blood cells, it produces bilirubin. It normally moves through the bile produced by the liver and into the bile ducts, past the gallbladder, and into the digestive system.
When bilirubin is not properly processed, it builds up in the bloodstream. This causes the skin and the whites of the eyes to turn yellow. This is called jaundice. Severely high levels of bilirubin can damage the brain and other organs.
People with DJS have lifelong mild jaundice that may be made worse by:
- Alcohol
- Birth control pills
- Environmental factors that affect the liver
- Infection
- Pregnancy
Symptoms
Mild jaundice, which may not appear until puberty or adulthood, is most often the only symptom of DJS.
Exams and Tests
The following tests can help diagnose this syndrome:
-
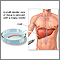
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver enzyme levels (blood test)
-
Serum bilirubin
Serum bilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinary coproporphyrin levels
Urinary coproporphyrin levels
Porphyrins are natural chemicals in the body that help form many important substances in the body. One of these is hemoglobin, the protein in red bl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
No specific treatment is required.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook is very positive. DJS generally does not shorten a person's lifespan.
Possible Complications
Complications are unusual, but may include the following:
- Reduced liver function
- Severe jaundice
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if any of the following occurs:
- Jaundice is severe
- Jaundice gets worse over time
-
You also have
abdominal pain
or other symptoms (which may be a sign that another disorder is causing the jaundice)
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Prevention
If you have a family history of DJS, genetic counseling may be helpful if you plan to have children.
References
Berk PD, Korenblat KM. Approach to the patient with jaundice or abnormal liver tests. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 147.
Lidofsky SD. Jaundice. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 21.
-
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
Review Date: 8/22/2016
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.