VIPoma
Vasoactive intestinal peptide-producing tumor; VIPoma syndrome; Pancreatic endocrine tumor
VIPoma is a very rare cancer that usually grows from cells in the pancreas called islet cells.
Causes
VIPoma causes cells in the pancreas to produce a high level of a hormone called vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). This hormone increases secretions from the intestines. It also relaxes some of the smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal system.
The exact cause of VIPomas is not known.
VIPomas are often diagnosed in adults, most commonly at age 50. Women are more likely to be affected than men. This cancer is rare. Each year, only about 1 in 10 million people are diagnosed with a VIPoma.
Symptoms
Symptoms of VIPoma may include any of the following:
-
Abdominal pain
and cramping
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diarrhea (watery, and often in large amounts)
-
Dehydration
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it should. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how muc...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Flushing or redness of the face
-
Muscle cramps due to low blood calcium (
hypokalemia
)
Hypokalemia
Low potassium level is a condition in which the amount of potassium in the blood is lower than normal. The medical name of this condition is hypokal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
Tests that may be done include:
-
Blood chemistry tests (basic or
comprehensive metabolic panel
)
Comprehensive metabolic panel
A comprehensive metabolic panel is a group of blood tests. They provide an overall picture of your body's chemical balance and metabolism. Metaboli...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the abdomen
CT scan of the abdomen
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging method. This test uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomog...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the abdomen
MRI of the abdomen
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Stool examination for cause of diarrhea and
electrolyte
levels
Electrolyte
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - VIP level in the blood
Treatment
The first goal of treatment is to correct dehydration. Fluids are often given through a vein (intravenous fluids) to replace fluids lost through diarrhea.
The next goal is to slow the diarrhea. Medicines can help control diarrhea. One such medicine is octreotide. It is a manmade form of a natural hormone that blocks the action of VIP.
The best chance of a cure is surgery to remove the tumor. If the tumor has not spread to other organs, surgery can often cure the condition.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group . Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Cancer support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society -- www. cancer. orgCancerCare -- www. cancercare. or...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Surgery can usually cure VIPomas. But, in one third to one half of people, the tumor has spread by the time of diagnosis and cannot be cured.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Cancer spread (metastasis)
- Cardiac arrest from low blood potassium level
- Dehydration
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you have watery diarrhea for more than 2 to 3 days, call your provider.
References
National Cancer Institute. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (islet cell tumors) treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. Cancer.gov Web site. Updated April 30, 2015. www.cancer.gov/types/pancreatic/hp/pnet-treatment-pdq#section/all . Accessed December 21, 2016.
Schneider DF, Mazeh H, Lubner SJ, Jaume JC, Chen H. Cancer of the endocrine system. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 71.
Vella A. Gastrointestinal hormones and gut endocrine tumors. In: Melmed S, Polonsky KS, Larsen PR, Kronenberg HM, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology . 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 38.
-
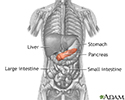
Pancreas - illustration
The pancreas is an elongated, tapered gland that is located behind the stomach and secretes digestive enzymes and the hormones insulin and glucagon.
Pancreas
illustration
Review Date: 11/10/2016
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.