Parapneumonic pleural effusion
Pleural effusion - pneumonia
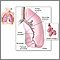
Pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid in the pleural space. The pleural space is the area between the layers of the tissue lining the lung and the chest cavity.
Pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.
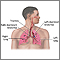
With parapneumonic pleural effusion, the fluid buildup is caused pneumonia .
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a breathing (respiratory) condition in which there is an infection of the lung. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). ...
Causes
Pneumonia, most commonly from bacteria, causes parapneumonic pleural effusion.
Symptoms
Symptoms can include any of the following:
- Chest pain, usually a sharp pain that is worse with cough or deep breaths
- Cough with sputum
- Fever
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. The provider will also listen to your lungs with a stethoscope and tap (percuss) your chest and upper back.
The following tests may help to confirm a diagnosis:
-
Complete blood count (CBC) blood test
Complete blood count (CBC) blood test
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest CT scan
- Chest x-ray
-
Thoracentesis
(a sample of fluid is removed with a needle inserted between the ribs)
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid from the space between the lining of the outside of the lungs (pleura) and the wall of the chest....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Ultrasound of the chest and heart
Treatment
Antibiotics are prescribed to treat the pneumonia.
If the person has shortness of breath, thoracentesis might be used to drain the fluid. If better drainage of the fluid is needed due to more severe infection, a drain tube can be inserted.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This condition improves when the pneumonia improves.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Lung damage
-
Infection that turns into an abscess, called an
empyema
, which will need to be drained with a chest tube
Empyema
Empyema is a collection of pus in the space between the lung and the inner surface of the chest wall (pleural space).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Collapsed lung (
pneumothorax
) after thoracentesis
Pneumothorax
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung, between the lung and chest wall. This bui...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have symptoms of pleural effusion.
Call your provider or go to the emergency room if shortness of breath or difficulty breathing occurs right after thoracentesis.
References
Nicks BA, Manthey DE. Pleural effusion. In: Adams JG, ed. Emergency Medicine: Clinical Essentials . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:chap 52.
Septimus EJ. Pleural effusion and empyema. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Updated Edition . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 70.
-
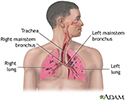
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 8/21/2016
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.