Viral pneumonia
Pneumonia - viral; Walking pneumonia - viral
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ.
Viral pneumonia is caused by a virus.
Causes
Viral pneumonia is more likely to occur in young children and older adults. This is because their bodies have a harder time fighting off the virus than people with a strong immune system.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a breathing (respiratory) condition in which there is an infection of the lung. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). ...
Viral pneumonia is most often caused by one of several viruses:
- Adenovirus
- Influenza
- Parainfluenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Measles
Serious viral pneumonia is more likely to happen in those with a weakened immune system, such as:
- Babies who are born too early
- Children with heart and lung problems
- People who have HIV/AIDS
- People receiving chemotherapy for cancer, or other medicines that weaken the immune system
- People who have had an organ transplant
Symptoms
Symptoms of viral pneumonia often begin slowly and may not be severe at first.
The most common symptoms of pneumonia are:
-
Cough
(with some pneumonias you may cough up mucus, or even bloody mucus)
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
, which may be mild or high
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shaking chills
-
Shortness of breath
(may only occur when you exert yourself)
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms include:
- Confusion, often in older people
- Excessive sweating and clammy skin
- Headache
- Loss of appetite, low energy, and fatigue
- Sharp or stabbing chest pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply or cough
- Fatigue
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about the symptoms.
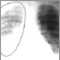
If the provider thinks you have pneumonia, you will also have a chest x-ray . This is because the physical exam may not be able to tell pneumonia from other respiratory infections.
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
Depending on how severe your symptoms are, other tests may be done, including:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
-
CT scan of the chest
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood cultures to check for viruses in the blood
- Bronchoscopy (rarely needed)
- Throat and nose swab tests to check for viruses such as the flu
-
Open lung biopsy
(only done in very serious illnesses when the diagnosis cannot be made from other sources)
Open lung biopsy
An open lung biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined for cancer, infection, or lung disease....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
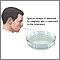
Sputum culture
(to rule out other causes)
Sputum culture
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Measuring
levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood
Levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in ...
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Antibiotics do not treat this type of lung infection. Medicines that treat viruses may work against some pneumonias caused by influenza and the herpes family of viruses. These medicines may be tried if the infection is caught early.
Treatment may also involve:
- Corticosteroid medicines
- Increased fluids
- Oxygen
- Use of humidified air
A hospital stay may be needed if you are unable to drink enough and to help with breathing if oxygen levels are too low.
People are more likely to be admitted to the hospital if they:
- Are older than 65 years or are children
- Are unable to care for themselves at home, eat, or drink
- Have another serious medical problem, such as a heart or kidney problem
- Have been taking antibiotics at home and are not getting better
- Have severe symptoms
However, many people can be treated at home. You can take these steps at home:
-
Control your fever with aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen), or acetaminophen. DO NOT give aspirin to children because it may cause a dangerous illness called
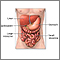
Reye syndrome
.
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome has occurred in ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - DO NOT take cough medicines without first talking to your provider. Cough medicines may make it harder for your body to cough up sputum.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen secretions and bring up phlegm.
- Get a lot of rest. Have someone else do chores.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most cases of viral pneumonia are mild and get better without treatment within 1 to 3 weeks. Some cases are more serious and require a hospital stay.
Possible Complications
More serious infections can result in respiratory failure, liver failure, and heart failure. Sometimes, bacterial infections occur during or just after viral pneumonia, which may lead to more serious forms of pneumonia.
Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if symptoms of viral pneumonia develop or your condition gets worse after starting to improve.
Prevention
Wash your hands often, after blowing your nose, going to the bathroom, diapering a baby, and before eating or preparing food.
DO NOT smoke. Tobacco damages your lungs' ability to ward off infection.
A drug called palivizumab (Synagis) may be given to children under 24 months old to prevent RSV.
The flu vaccine , is given each year to prevent pneumonia caused by the flu virus. Those who are older and those with diabetes, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cancer, or weakened immune systems should be sure to get the flu vaccine.
Flu vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-...

If your immune system is weak, stay away from crowds. Ask visitors who have a cold to wear a mask and wash their hands.
References
Lee FE, Treanor JJ. Viral infections. In: Broaddus VC, Mason RJ, Ernst JD, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 32.
Parameswaran GI, Sethi S. Viral pneumonia. In: Spiro SG, Silvestri GA, Agustí A, eds. Clinical Respiratory Medicine . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 25.
-
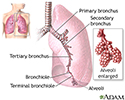
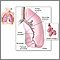
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
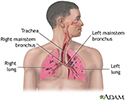
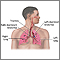
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
-
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 8/21/2016
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.