Genital injury
Scrotal trauma; Straddle injury; Toilet seat injury
A genital injury is an injury to male or female sex organs, especially those outside the body. It also refers to injury in the area between the legs, called the perineum.
Considerations
Injury to the genitals can be very painful. It may cause a lot of bleeding. Such injury can affect the reproductive organs and the bladder and urethra.
Damage may be temporary or permanent.
Causes
Genital injury can occur in both women and young girls. It may be caused by placing items into the vagina. Young girls (usually less than 4 years of age) may do this during normal exploration of the body. Objects used may include toilet tissue, crayons, beads, pins, or buttons.
It is important to rule out sexual abuse, rape, and assault. The health care provider should ask the girl how the object was placed there.
In men and young boys, common causes of genital injury include:
- Having the toilet seat fall down onto the area
- Getting the area caught in a pant zipper
- Straddle injury - falling and landing with the legs on each side of a bar, such as a monkey bar or the middle of a bicycle
Symptoms
-
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding
- Bruising
- Change in shape of the affected area
-
Faintness
Faintness
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Foul-smelling
vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge refers to secretions from the vagina. The discharge may be:Thick, pasty, or thinClear, cloudy, bloody, white, yellow, or greenOdor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Object embedded in a body opening
-
Groin pain
or genital pain (can be extreme)
Groin pain
Groin pain refers to discomfort in the area where the abdomen ends and the legs begin. This article focuses on groin pain in men. The terms "groin"...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling
- Urine drainage
- Vomiting
-
Urination that is painful
or the inability to urinate
Urination that is painful
Painful urination is any pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when passing urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wound
First Aid
Keep the person calm. Be sensitive to privacy. Cover the injured area while giving first aid.
Control bleeding by using direct pressure. Place a clean cloth or sterile dressing on any open wounds. If the vagina is bleeding severely, put sterile gauze or clean cloths on the area, unless a foreign body is suspected.
Apply cold compresses to help reduce swelling.
If the testicles have been injured, support them with a sling made from towels. Place them on a padded cloth such as a diaper.
Testicles
The testes are 2 egg-shaped male reproductive organs located in the scrotum. They produce sperm and the male hormone, testosterone.
If there is an object stuck in a body opening or wound, leave it alone and seek medical attention. Taking it out may cause more damage.
Do Not
Do not try to remove an object by yourself. Seek medical help immediately.
Never volunteer your thoughts on how you think the injury happened. If you think the injury was the result of assault or abuse, do NOT let the person change clothes or take a bath or shower. See immediate medical help.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
A straddle injury is damage to the testicle or urinary tract. Immediately get medical help if there is:
- A lot of swelling or bruising
- Blood in the urine
Seek immediate medical help if there is a genital injury and:
- Pain, bleeding, or swelling
- A concern about sexual abuse
- Problems urinating
- Blood in the urine
Prevention
Teach safety to young children and create a safe environment for them. Also, keep small objects out of the reach of toddlers.
References
Gerber GS, Brendler CB. Evaluation of the urologic patient: History, physical examination, and the urinalysis. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh Urology . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 3.
-
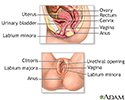
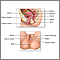
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
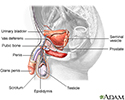
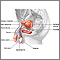
Male reproductive anatomy - illustration
The male reproductive structures include the penis, the scrotum, the seminal vesicles and the prostate.
Male reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
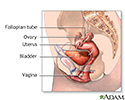
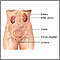
Normal female anatomy - illustration
The vagina is a thin-walled tube which lies between the bladder and rectum. It is often called the birth canal, since it provides the passageway of delivery of an infant.
Normal female anatomy
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Male reproductive anatomy - illustration
The male reproductive structures include the penis, the scrotum, the seminal vesicles and the prostate.
Male reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Normal female anatomy - illustration
The vagina is a thin-walled tube which lies between the bladder and rectum. It is often called the birth canal, since it provides the passageway of delivery of an infant.
Normal female anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 12/2/2014
Reviewed By: Jennifer Sobol, DO, Urologist with the Michigan Institute of Urology, West Bloomfield, MI. Review provided by VeriMed Healtcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.