Angioplasty and stent - heart - discharge
Drug-eluting stents - discharge; PCI - discharge; Percutaneous coronary intervention - discharge; Balloon angioplasty - discharge; Coronary angioplasty - discharge; Coronary artery angioplasty - discharge; Cardiac angioplasty - discharge; PTCA - discharge; Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty - discharge; Heart artery dilatation - discharge; Angina angioplasty - discharge; Heart attack angioplasty - discharge; CAD angioplasty - discharge
When You're in the Hospital
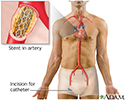
You had angioplasty when you were in the hospital. You may have also had a stent placed. Both of these were done to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply blood to your heart. You may have had a heart attack or angina (chest pain) before the procedure.
Heart attack
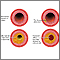
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
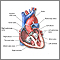
Angina
Angina is a type of chest discomfort or pain due to poor blood flow through the blood vessels (coronary vessels) of the heart muscle (myocardium). Th...
What to Expect at Home
You may have pain in your groin area, arm, or wrist. This is from the catheter (flexible tube) that was inserted to do the procedure. You may also have some bruising around and below the incision.
The chest pain and shortness of breath you likely had before the procedure should be much better now.
Self-care
In general, people who have angioplasty can walk around within 6 hours after the procedure. Complete recovery takes a week or less. Keep the area where the catheter was inserted dry for 24 to 48 hours.
If the doctor put the catheter in through your groin:
- Walking short distances on a flat surface is OK. Limit going up and down stairs to around 2 times a day for the first 2 to 3 days.
- DO NOT do yard work, drive, squat, carry heavy objects, or play sports for at least 2 days, or until your health care provider tells you it is safe.
If the doctor put the catheter in your arm or wrist:
- DO NOT lift anything heavier than 10 pounds (4.5 kg) (a little more than a gallon of milk) with the arm that had the catheter.
- DO NOT do any heavy pushing, pulling or twisting with that arm.
For a catheter in your groin, arm, or wrist:
- Avoid sexual activity for 2 to 5 days. Ask your provider when it will be OK to start again.
- DO NOT take a bath or swim for the first week. You may take showers, but make sure the area where the catheter was inserted does not get wet for the first 24 to 48 hours.
- You should be able to return to work in 2 to 3 days if you do not do heavy work.
You will need to care for your incision.
- Your provider will tell you how often to change your dressing.
- If your incision bleeds or swells up, lie down and put pressure on it for 30 minutes.
Angioplasty does not cure the cause of the blockage in your arteries. Your arteries may become narrow again. Eat a heart-healthy diet, exercise, stop smoking (if you smoke), and reduce stress to help lower your chances of having a blocked artery again. Your provider may give you medicine to help lower your cholesterol.
Most people take aspirin together with another antiplatelet medicine such as clopidogrel (Plavix), prasugrel (Efient), or ticagrelor (Brilinta) after this procedure. These medicines are blood thinners. They keep your blood from forming clots in your arteries and stent. A blood clot can lead to a heart attack. Take the medicines exactly as your provider tells you. DO NOT stop taking them without talking with your provider first.
Aspirin
Blood thinners - aspirin; Antiplatelet therapy - aspirin
Clopidogrel
Blood thinners - clopidogrel; Antiplatelet therapy - clopidogrel; Thienopyridines
You should know how to take care of your angina if it returns.
Take care of your angina
Acute coronary syndrome - chest pain; Coronary artery disease - chest pain; CAD - chest pain; Coronary heart disease - chest pain; ACS - chest pain; ...
Make sure you have a follow-up appointment scheduled with your heart doctor (cardiologist).
Your doctor may refer you to a cardiac rehabilitation program. This will help you learn how to slowly increase your exercise . You will also learn how to take care of your angina and care for yourself after a heart attack .
Slowly increase your exercise
Chest pain - discharge; Stable angina - discharge; Chronic angina - discharge; Variant angina - discharge; Angina pectoris - discharge; Accelerating ...

Take care of your angina
Chest pain - discharge; Stable angina - discharge; Chronic angina - discharge; Variant angina - discharge; Angina pectoris - discharge; Accelerating ...

Care for yourself after a heart attack
Myocardial infarction - discharge; MI - discharge; Coronary event - discharge; Infarct - discharge; Acute coronary syndrome - discharge; ACS - discha...
When to Call the Doctor
Call your doctor if:
- There is bleeding at the catheter insertion site that does not stop when you apply pressure.
- There is swelling at the catheter site.
- Your leg or arm below where the catheter was inserted changes color, becomes cool to touch, or is numb.
- The small incision for your catheter becomes red or painful, or yellow or green discharge is draining from it.
- You have chest pain or shortness of breath that does not go away with rest.
- Your pulse feels irregular -- very slow (fewer than 60 beats), or very fast (over 100 to 120 beats) a minute.
- You have dizziness, fainting, or you are very tired.
- You are coughing up blood or yellow or green mucus.
- You have problems taking any of your heart medicines.
- You have chills or a fever over 101°F (38.3°C).
References
Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol . 2014;64(24):e139-e228. PMID: 25260718 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25260718 .
Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation . 2012;126(25):e354-e471. PMID: 23166211 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23166211 .
O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation . 2013;127(4):529-555. PMID: 23247303 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23247303 .
Vandvik PO, Lincoff AM, Gore JM, et al. Primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest . 2012;141(2 Suppl):e637S-e668S. PMID: 22315274 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22315274 .
-
Balloon angioplasty - short segment
Animation
-
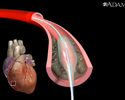
Coronary artery stent - illustration
A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that is placed inside a coronary artery to help keep the artery open. To place the stent, a small incision can be made in the groin area to reach the artery there. A catheter is guided through the groin artery into an area of the coronary artery which is blocked. The stent is inserted along with a balloon catheter and expands when the balloon is inflated. The stent is then left there to help keep the artery open.
Coronary artery stent
illustration
-
Coronary artery stent - illustration
A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that is placed inside a coronary artery to help keep the artery open. To place the stent, a small incision can be made in the groin area to reach the artery there. A catheter is guided through the groin artery into an area of the coronary artery which is blocked. The stent is inserted along with a balloon catheter and expands when the balloon is inflated. The stent is then left there to help keep the artery open.
Coronary artery stent
illustration
-
Heart attack and acute coronary syndrome
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 8/2/2016
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.