Laser surgery - skin
Surgery using a laser
Laser surgery uses laser light to remove diseased tissues or treat bleeding blood vessels. Laser surgery may also be used to remove wrinkles, sunspots, tattoos, or birthmarks.
Description
A laser is a light beam that can be focused on a very small area. The laser heats cells in the area being treated until they "burst."
There are several types of lasers. Each laser has specific uses. The color of the light beam used is directly related to the type of surgery being performed and the color of the tissue being treated.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Laser surgery can be used to:
- Close small blood vessels to reduce blood loss
-
Remove
warts
,
moles
, sunspots, and tattoos
Warts
Warts are small, usually painless growths on the skin. Most of the time they are harmless. They are caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMoles
A birthmark is a skin marking that is present at birth. Birthmarks include cafe-au-lait spots, moles, and Mongolian spots. Birthmarks can be red or...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Reduce the appearance of skin wrinkles, scars, and other skin blemishes
- Remove dilated blood vessels from the face
- Remove hair
- Remove skin cells that could turn into cancer
Risks
Possible risks of laser surgery include:
- Cold sores if herpes simplex virus is already present
- Bleeding
- Problem not going away
- Infection
- Pain
- Scarring
- Skin color changes
Some laser surgery is done when you are asleep and pain free ( general anesthesia ). Talk to your health care provider about risks of laser surgery.
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you receive the...
After the Procedure
The success of laser surgery depends on the condition being treated. Talk to your health care provider about what you can expect.
You may need to keep your skin moisturized and out of the sun after treatment.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Recovery time depends on the surgery and your overall health. Ask your health care provider before surgery how much recovery time you will need.
References
James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Cutaneous laser surgery. In: James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 38.
Tung R, Vidimos A. Nonmelanoma skin cancer. In: Carey WD. Cleveland Clinic: Current Clinical Medicine . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2010.
-
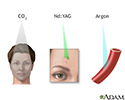
Laser therapy - illustration
A laser is used for many medical purposes. Because the laser beam is so small and precise, it enables physicians to safely treat specific tissue without injuring surrounding tissue. Some uses of the laser are retinal surgery, excision of lesions, and cauterization of vascular structures.
Laser therapy
illustration
-
Laser therapy - illustration
A laser is used for many medical purposes. Because the laser beam is so small and precise, it enables physicians to safely treat specific tissue without injuring surrounding tissue. Some uses of the laser are retinal surgery, excision of lesions, and cauterization of vascular structures.
Laser therapy
illustration
-
Skin wrinkles and blemishes
(In-Depth)
-
Melanoma and other skin cancers
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 12/2/2014
Reviewed By: Richard J. Moskowitz, MD, dermatologist in private practice, Mineola, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.