Hydrocephalus
Water on the brain
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling.
Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain."
Causes
Hydrocephalus is due to a problem with the flow of the fluid that surrounds the brain. This fluid is called the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF. The fluid surrounds the brain and spinal cord and helps cushion the brain.
CSF normally moves through the brain and the spinal cord and is soaked into the bloodstream. CSF levels in the brain can rise if:
- The flow of CSF is blocked.
- The fluid does not get properly absorbed into the blood.
- The brain makes too much of the fluid.
Too much CSF puts pressure on the brain. This pushes the brain up against the skull and damages brain tissue.
Hydrocephalus may begin while the baby is growing in the womb. It is common in babies who have a myelomeningocele, a birth defect in which the spinal column does not close properly.
Hydrocephalus may also be due to:
- Genetic defects
- Certain infections during pregnancy
In young children, hydrocephalus may be due to:
- Infections that affect the central nervous system (such as meningitis or encephalitis), especially in infants
- Bleeding in the brain during or soon after delivery (especially in premature babies)
- Injury before, during, or after childbirth, including subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Tumors of the central nervous system, including the brain or spinal cord
- Injury or trauma
Hydrocephalus most often occurs in children. Another type, called normal pressure hydrocephalus , may occur in adults and the elderly.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of spinal fluid inside the fluid chambers of the brain. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "Normal pressure hydroce...

Symptoms
Symptoms of hydrocephalus depend on:
- Age
- Amount of brain damage
- What is causing the buildup of CSF fluid
In infants, hydrocephalus causes the fontanelle (soft spot) to bulge and the head to be larger than expected. Early symptoms may also include:
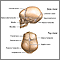
Fontanelle
A bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
- Eyes that appear to gaze downward
- Irritability
- Seizures
- Separated sutures
- Sleepiness
- Vomiting
Symptoms that may occur in older children can include:
- Brief, shrill, high-pitched cry
- Changes in personality, memory, or the ability to reason or think
- Changes in facial appearance and eye spacing
-
Crossed eyes
or uncontrolled eye movements
Crossed eyes
Strabismus is a disorder in which both eyes do not line up in the same direction. Therefore, they do not look at the same object at the same time. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty feeding
- Excessive sleepiness
- Headache
- Irritability, poor temper control
-
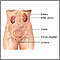
Loss of bladder control
(urinary incontinence)
Loss of bladder control
Urge incontinence occurs when you have a strong, sudden need to urinate. The bladder then squeezes, or spasms, and you lose urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of coordination and trouble walking
-
Muscle spasticity
(spasm)
Muscle spasticity
Strabismus is a disorder in which both eyes do not line up in the same direction. Therefore, they do not look at the same object at the same time. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Slow growth (child 0 to 5 years)
- Slow or restricted movement
-
Vomiting
Vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up is forcing the contents of the stomach ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will examine the baby. This may show:
- Stretched or swollen veins on the baby's scalp
- Abnormal sounds when the provider taps lightly on the skull, suggesting a problem with the skull bones
- All or part of the head may be larger than normal, often the front part
- Eyes that look "sunken in"
- White part of the eye appears over the colored area, making it look like a "setting sun"
- Reflexes may be normal
Repeated head circumference measurements over time may show that the head is getting bigger.
A head CT scan is one of the best tests for identifying hydrocephalus. Other tests that may be done include:
-
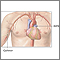
Arteriography
Arteriography
An arteriogram is an imaging test that uses x-rays and a special dye to see inside the arteries. It can be used to view arteries in the heart, brain...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brain scan using radioisotopes
- Cranial ultrasound (an ultrasound of the brain)
-
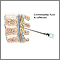
Lumbar puncture
and examination of the cerebrospinal fluid (rarely done)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skull x-rays
Skull x-rays
A skull x-ray is a picture of the bones surrounding the brain, including the facial bones, the nose, and the sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce or prevent brain damage by improving the flow of CSF.
Surgery may be done to remove a blockage, if possible.
If not, a flexible tube called a shunt may be placed in the brain to reroute the flow of CSF. The shunt sends CSF to another part of the body, such as the belly area, where it can be absorbed.
Other treatments may include:
- Antibiotics if there are signs of infection. Severe infections may require the shunt to be removed.
- A procedure called endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV), which relieves pressure without replacing the shunt.
-
Removing or burning away (
cauterizing
) the parts of the brain that produce CSF.
Cauterizing
Electrocauterization is the process of heating tissue with electricity.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
The child will need regular check-ups to make sure there are no further problems. Tests will be done regularly to check the child's development, and to look for intellectual, neurological, or physical problems.
Visiting nurses, social services, support groups, and local agencies can provide emotional support and help with the care of a child with hydrocephalus who has serious brain damage.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Without treatment, up to 6 in 10 people with hydrocephalus will die. Those who survive will have different amounts of intellectual, physical, and neurological disabilities.
The outlook depends on the cause. Hydrocephalus that is not due to an infection has the best outlook. People with hydrocephalus caused by tumors will often do very poorly.
Most children with hydrocephalus who survive for 1 year will have a fairly normal lifespan.
Possible Complications
The shunt may become blocked. Symptoms of such a blockage include headache and vomiting. Surgeons may be able to help the shunt open without having to replace it.
There may be other problems with the shunt, such as kinking, tube separation, or infection in the area of the shunt.
Other complications may include:
- Complications of surgery
- Infections such as meningitis or encephalitis
- Intellectual impairment
- Nerve damage (decrease in movement, sensation, function)
- Physical disabilities
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical care right away if your child has any symptoms of this disorder. Go to the emergency room or call 911 if emergency symptoms occur, such as:
- Breathing problems
- Extreme drowsiness or sleepiness
- Feeding difficulties
- Fever
- High-pitched cry
- No pulse (heartbeat)
- Seizures
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Vomiting
You should also call your provider if:
- The child has been diagnosed with hydrocephalus and the condition gets worse.
- You are unable to care for the child at home.
Prevention
Protect the head of an infant or child from injury. Prompt treatment of infections and other disorders associated with hydrocephalus may reduce the risk of developing the disorder.
References
Kinsman SL, Johnston MV. Congenital anomalies of the central nervous system. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 591.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Daroff RB, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, eds. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 88.
-
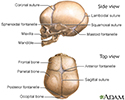
Skull of a newborn - illustration
The "sutures" or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the "soft spot" in young infants.
Skull of a newborn
illustration
-
Skull of a newborn - illustration
The "sutures" or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the "soft spot" in young infants.
Skull of a newborn
illustration
Review Date: 11/19/2015
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.