Retroversion of the uterus
Uterus retroversion; Malposition of the uterus; Tipped uterus; Tilted uterus
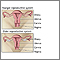
Retroversion of the uterus occurs when a woman's uterus (womb) tilts backward rather than forward. It is commonly called a "tipped uterus."
Causes
Retroversion of the uterus is common. One in 5 women has this condition.The problem may also occur due to weakening of the pelvic ligaments at the time of menopause . An enlarged uterus can also be caused by pregnancy or a tumor .
Menopause
Menopause is the time in a woman's life when her periods (menstruation) stop. Most often, it is a natural, normal body change that most often occurs...
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Scar tissue in the pelvis (pelvic adhesions) can also hold the uterus in a retroverted position. Scarring may come from:
-
Endometriosis
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when cells from the lining of your womb (uterus) grow in other areas of your body. This can cause pain, heavy bleeding, bleedin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection in uterus or tubes
- Pelvic surgery
Symptoms
Retroversion of the uterus almost never causes any symptoms.
Rarely, it may cause pain or discomfort.
Exams and Tests
A pelvic exam will show the position of the uterus. However, a tipped uterus can sometimes be mistaken for a pelvic mass or a growing fibroid . A rectovaginal exam may be used to distinguish between a mass and a retroverted uterus.
Fibroid
Uterine fibroids are tumors that grow in a woman's womb (uterus). These growths are typically not cancerous (benign).

An ultrasound test can be used to see the exact position of the uterus.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
Treatment
Treatment is not needed most of the time. Underlying disorders, such as endometriosis or adhesions, should be treated as needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
In most cases, the condition does not cause problems.
Possible Complications
Atypical positioning of the uterus may be caused by endometriosis, salpingitis, or pressure from a growing tumor.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have ongoing pelvic pain or discomfort.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent the problem. Early treatment of uterine infections or endometriosis may reduce the chances of a change in the position of the uterus.
References
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Female genitalia. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Siedel's Guide to Physical Examination . 8th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby; 2015:chap 18.
Lobo RA. Endometriosis: etiology, pathology, diagnosis, management. In: Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Katz VL, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2012:chap 19.
-
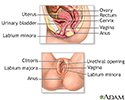
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
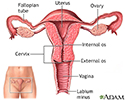
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Review Date: 5/16/2016
Reviewed By: Irina Burd, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Gynecology and Obstetrics at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.