Alveolar abnormalities
Alveolar abnormalities are changes in the tiny air sacs in the lungs, called alveoli. Alveoli allow oxygen to enter the blood. They are very thin to let oxygen move from the lungs to the blood vessels, and for carbon dioxide to be removed from the blood vessels to the lungs.
Depending on the disease, alveoli may:
- Collapse
- Fuse together
- Develop thickened linings
- Fill with fluid
- Fill with blood
- Fill with pus
- Get destroyed
References
Albertine KH. Anatomy of the lungs. In: Broaddus VC, Mason RJ, Ernst JD, et al, eds.
Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine
. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 1.
Costanzo LS. Respiratory physiology. In: Costanzo LS, ed. Physiology . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 5.
-
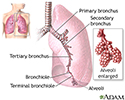
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
Review Date: 6/22/2015
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.