Retinoblastoma
Tumor - retina; Cancer - retina; Eye cancer - retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare, cancerous tumor of a part of the eye called the retina.
Causes
Retinoblastoma is caused by a mutation in a gene that controls how cells divide. As a result, cells grow out of control and become cancerous.
In about half the cases, this mutation develops in a child whose family has never had eye cancer. In other cases, the mutation occurs in several family members. If the mutation runs in the family, there is a 50% chance that an affected person's children will also have the mutation. These children will therefore have a high risk of developing retinoblastoma themselves.
The cancer most often affects children younger than 6 years old. It is most commonly diagnosed in children 1 to 2 years old.
Symptoms
One or both eyes may be affected.
The pupil of the eye may appear white or have white spots. A white glow in the eye is often seen in photographs taken with a flash. Instead of the typical "red eye" from the flash, the pupil may appear white or distorted.
Other symptoms can include:
-
Crossed eyes
Crossed eyes
Strabismus is a disorder in which both eyes do not line up in the same direction. Therefore, they do not look at the same object at the same time. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Double vision
- Eyes that do not align
- Eye pain and redness
-
Poor vision
Poor vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: HalosBlurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Differing
iris
colors in each eye
Iris
The iris is the colored part of the eye. It is located between the cornea and lens. The round, central opening of the iris is called the pupil. Ve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If the cancer has spread, bone pain and other symptoms may occur.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a complete physical exam, including an eye exam. The following tests may be done:
-
CT scan
or
MRI of the head
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eye exam with dilation of the pupil
-
Ultrasound
of the eye (
head and eye echoencephalogram
)
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHead and eye echoencephalogram
An eye and orbit ultrasound is a test to look at the eye area. It also measures the size and structures of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment options depend on the size and location of the tumor:
-
Small tumors may be treated by
laser surgery
or cryotherapy (freezing).
Laser surgery
Laser therapy is a medical treatment that uses a strong beam of light to cut, burn, or destroy tissue. The term LASER stands for "Light Amplificatio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radiation is used for both a tumor that is within the eye and for larger tumors.
-
Chemotherapy
may be needed if the tumor has spread beyond the eye.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The eye may need to be removed (a procedure called enucleation) if the tumor does not respond to other treatments. In some cases, it may be the first treatment.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the cancer has not spread beyond the eye, almost all people can be cured. A cure, however, may require aggressive treatment and even removal of the eye in order to be successful.
If the cancer has spread beyond the eye, the likelihood of a cure is lower and depends on how the tumor has spread.
Possible Complications
Blindness can occur in the affected eye. The tumor can spread to the eye socket through the optic nerve. It may also spread to the brain, lungs, and bones.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if signs or symptoms of retinoblastoma are present, especially if your child's eyes look abnormal or appear abnormal in photographs.
Prevention
Genetic counseling can help families understand the risk for retinoblastoma. It is especially important when more than 1 family member has had the disease, or if retinoblastoma occurs in both eyes.
References
Augsburger JJ, Bornfeld N, Correa ZM. Retinoblastoma. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 8.1.
Karcioglu ZA, Haik BG. Eye, orbit, and adnexal structures. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 67.
National Cancer Institute: PDQ childhood astrocytomas treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Date last modified August 14, 2015. www.cancer.gov/types/brain/hp/child-astrocytoma-treament-pdq . Accessed: January 19, 2016.
-
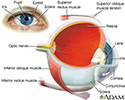
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle tunic layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle tunic layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
Review Date: 12/23/2015
Reviewed By: Adam S. Levy, MD, Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, The Children's Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.