Toxic megacolon
Toxic dilation of the colon; Megarectum; Inflammatory bowel disease - toxic megacolon; Crohn disease - toxic megacolon; Ulcerative colitis - toxic megacolon
Toxic megacolon occurs when swelling and inflammation spread into the deeper layers of your colon. As a result, the colon stops working and widens. In severe cases, the colon may rupture.
Causes
The term "toxic" means that this problem is very dangerous. Toxic megacolon may occur in people with an inflamed colon due to:
-
Ulcerative colitis
, or
Crohn disease
that is not well controlled
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCrohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections of the colon
Other forms of megacolon include pseudo-obstruction, acute colonic ileus, or congenital colonic dilation. These conditions do not involve an infected or inflamed colon.
Symptoms
The rapid widening of the colon may cause the following symptoms to occur over a short period of time:
-
Painful and
distended abdomen
Distended abdomen
A swollen abdomen is when your belly area is bigger than usual.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever
If the colon ruptures, symptoms may include
- Rapid heart rate
-
Shock
, when a bodywide infection leads to dangerously low blood pressure
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means that the cells and organs...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A physical exam may reveal signs of septic shock . The health care provider will notice tenderness in the abdomen and possible loss of bowel sounds .
Septic shock
Septic shock is a serious condition that occurs when a body-wide infection leads to dangerously low blood pressure.
Bowel sounds
Abdominal sounds are the noises made by the intestines.
Tests:
-
Abdominal x-ray
, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI scan
Abdominal x-ray
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the spleen, stomach, and intestines. When the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood electrolytes
-
Complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment of the disorder that led to toxic megacolon may be started, including:
- Steroids and other medicines that suppress the immune system
- Antibiotics
If you have septic shock, you will be admitted to the intensive care unit of the hospital. Treatment may include:
- Breathing machine (mechanical ventilation)
- Dialysis for kidney failure
- Drugs to treat low blood pressure, infection, or poor blood clotting
- Fluids given directly into a vein (intravenously)
- Oxygen
If rapid widening is allowed to continue, an opening or rupture can form in the colon. Therefore, most cases of toxic megacolon will need surgery to remove a part of or the entire colon.
Surgery
Large bowel resection is surgery to remove all or part of your large bowel. This surgery is also called colectomy. The large bowel is also called t...
You may receive antibiotics to prevent sepsis (a severe infection).
Sepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.

Outlook (Prognosis)
If the condition does not improve, it can be life threatening. In this case, a colectomy is usually needed.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Perforation of the colon
- Sepsis
- Shock
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if you develop severe abdominal pain, especially if you also have:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Fever
- Frequent diarrhea
- Rapid heart rate
- Tenderness when the abdomen is pressed
Prevention
Treating diseases that cause toxic megacolon, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn disease, can prevent this condition.
References
Lichtenstein GR. Inflammatory bowel disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 141.
Marrero F. Severe complications of inflammatory bowel disease. Med Clin North Am . 2008;92:671-686. PMID: 18387381 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18387381 .
Peterson MA. Disorders of the large intestine. In: Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Walls RM, et al, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 95.
-
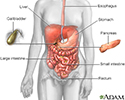
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
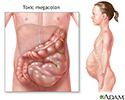
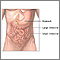
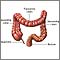
Toxic megacolon - illustration
Toxic megacolon is characterized by extreme inflammation and distention of the colon. Common symptoms are pain, distention of the abdomen, fever, rapid heart rate, and dehydration. This is a life-threatening complication that requires immediate medical treatment.
Toxic megacolon
illustration
-
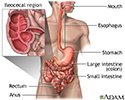
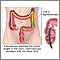
Crohn's disease - affected areas - illustration
The inflammation of Crohn disease is nearly always found in the ileocecal region. The ileocecal region consists of the last few inches of the small intestine (the ileum), which moves digesting food to the beginning portion of the large intestine (the cecum). However, Crohn disease can occur anywhere along the digestive tract.
Crohn's disease - affected areas
illustration
-
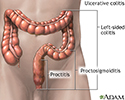
Ulcerative colitis - illustration
Ulcerative colitis is categorized according to location: Proctitis involves only the rectumProctosigmoiditis affects the rectum and sigmoid colonLeft-sided colitis encompasses the entire left side of the large intestinePancolitis inflames the entire colon Proctitis involves only the rectum Proctosigmoiditis affects the rectum and sigmoid colon Left-sided colitis encompasses the entire left side of the large intestine Pancolitis inflames the entire colon
Ulcerative colitis
illustration
-
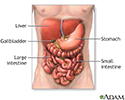
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Toxic megacolon - illustration
Toxic megacolon is characterized by extreme inflammation and distention of the colon. Common symptoms are pain, distention of the abdomen, fever, rapid heart rate, and dehydration. This is a life-threatening complication that requires immediate medical treatment.
Toxic megacolon
illustration
-
Crohn's disease - affected areas - illustration
The inflammation of Crohn disease is nearly always found in the ileocecal region. The ileocecal region consists of the last few inches of the small intestine (the ileum), which moves digesting food to the beginning portion of the large intestine (the cecum). However, Crohn disease can occur anywhere along the digestive tract.
Crohn's disease - affected areas
illustration
-
Ulcerative colitis - illustration
Ulcerative colitis is categorized according to location: Proctitis involves only the rectumProctosigmoiditis affects the rectum and sigmoid colonLeft-sided colitis encompasses the entire left side of the large intestinePancolitis inflames the entire colon Proctitis involves only the rectum Proctosigmoiditis affects the rectum and sigmoid colon Left-sided colitis encompasses the entire left side of the large intestine Pancolitis inflames the entire colon
Ulcerative colitis
illustration
-
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
Review Date: 10/27/2015
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist with Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.